HCOOCH CH2 H2O: Reaction of Methyl Formate and Water
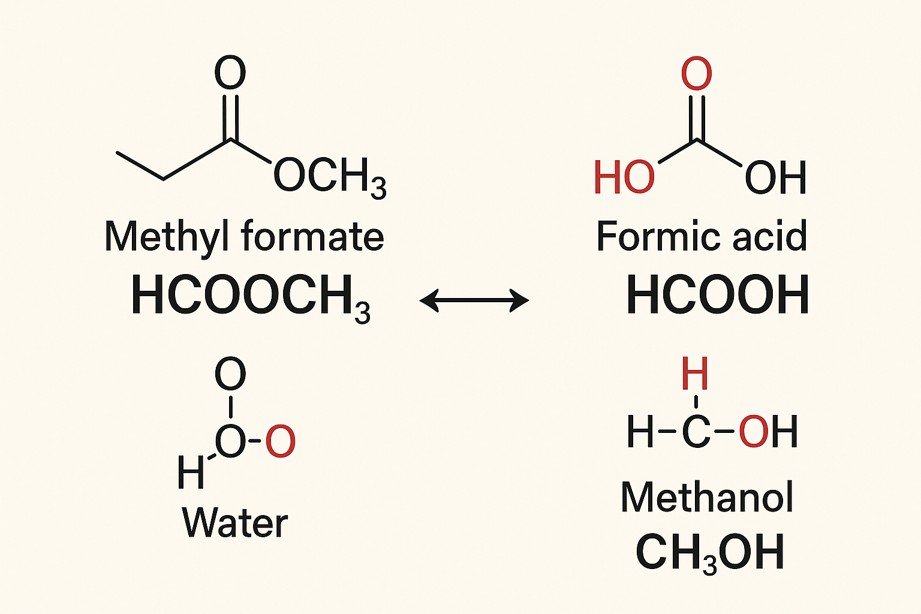
The formula HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O looks confusing, but it really refers to the reaction between methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) and water (H₂O).
This is a common type of chemical change called ester hydrolysis — when an ester reacts with water to make an acid and an alcohol.
The main chemical equation is:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O ⇌ HCOOH + CH₃OH\text{HCOOCH₃ + H₂O ⇌ HCOOH + CH₃OH}
-
HCOOCH₃ → Methyl formate (an ester)
-
H₂O → Water
-
HCOOH → Formic acid
-
CH₃OH → Methanol
This reaction is important in organic chemistry and industry, as it helps make useful products like formic acid and methanol.

2. What Is Methyl Formate?
Methyl formate is a colorless, sweet-smelling liquid. It is made when formic acid reacts with methanol.
It is used as a solvent, foam-blowing agent, and chemical raw material.
Basic Information
| Property | Detail |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | HCOOCH₃ |
| Molar Mass | 60.05 g/mol |
| Structure | H–C(=O)–O–CH₃ |
| Functional Group | Ester (–COO–) |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Sweet, ether-like |
| Boiling Point | 31.5 °C |
| Solubility | Mixes easily with water |
Because it mixes with water, methyl formate can react with it easily in the hydrolysis process.
3. The Reaction Between Methyl Formate and Water
The reaction makes formic acid and methanol:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH\text{HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH}
| Reactant | Type | Product | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCOOCH₃ | Ester | HCOOH | Acid |
| H₂O | Water | CH₃OH | Alcohol |
This reaction can also go in the reverse direction, turning acid and alcohol back into the ester (this is called esterification).
4. How the Reaction Works (Mechanism)
There are two main ways the reaction can happen — in acid or base conditions.
Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
-
The acid adds a proton (H⁺) to the ester’s oxygen.
-
This makes the carbon atom easier for water to attack.
-
Water attacks, forming a short-lived middle compound.
-
The bond breaks, forming formic acid and methanol.
-
The acid is freed again, ready to help another reaction.
Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
-
A hydroxide ion (OH⁻) attacks the ester carbon.
-
The molecule splits, giving a formate ion and methanol.
-
The formate ion turns into formic acid when it gets a proton (H⁺).
Note: The base reaction goes one way only — it does not easily reverse.
Read also: BinusCX
5. Things That Affect the Reaction
Several factors change how fast or how well the reaction works.
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Catalyst | Acids or bases speed up the reaction. |
| Temperature | Warmer temperatures make it go faster. |
| Water Amount | More water gives more formic acid and methanol. |
| Pressure | Keeps the reactants in liquid form. |
| Solvent Type | Polar (water-like) solvents make the reaction easier. |
Helpful Tips
-
Use a small amount of acid like H₂SO₄ as a catalyst.
-
Keep the reaction warm but not too hot (around 40–50 °C).
-
Add extra water to make sure the ester breaks down completely.
6. Uses and Applications
Methyl formate and its products are used in many areas of industry and daily life.
| Use | Description | Why It’s Useful |
|---|---|---|
| Formic Acid Production | Hydrolysis of methyl formate makes formic acid. | Efficient and easy to control. |
| Solvent | Used to dissolve resins and oils. | Low toxicity, evaporates quickly. |
| Foam Production | Blowing agent for polyurethane foams. | Replaces harmful CFC gases. |
| Intermediate Chemical | Used to make other compounds like DMF. | Important in chemical industries. |
| Energy Research | Can release hydrogen gas when decomposed. | May help in clean-energy storage. |
Green Chemistry Benefits
-
Methyl formate breaks down naturally.
-
Low global-warming potential.
-
Recyclable methanol by-product.
-
Water is a safe and clean reactant.
7. Safety and Environmental Information
Methyl formate is useful but needs careful handling.
Dangers
-
Flammable: Can catch fire easily.
-
Inhalation: Breathing large amounts can cause dizziness.
-
Skin/Eye contact: May cause redness or irritation.
Safety Rules
-
Work in a well-ventilated place.
-
Keep away from open flames or sparks.
-
Wear gloves, goggles, and lab coat.
-
Store in a cool, dry place.
Environmental Points
| Property | Result |
|---|---|
| Ozone Damage | None |
| Breakdown | Fast (forms CO₂ and formic acid) |
| Global Warming Effect | Very low |
| Waste Handling | Recycle methanol, neutralize acids |
8. Modern Research and Developments
Scientists continue to study this reaction to make it cleaner and more efficient.
New Catalysts
-
Solid acids like zeolites replace strong liquid acids.
-
Ionic liquids work as both solvent and catalyst.
-
Enzymes help the reaction happen at room temperature.
Industrial Improvements
-
Continuous-flow systems save energy.
-
Methanol is recycled automatically.
-
Safer and cheaper production methods are being developed.
Space Chemistry
Methyl formate has been found in outer space!
It is detected in clouds of gas and dust, showing that even in space, organic molecules can form naturally.
Clean Energy Research
Methyl formate can be used as a hydrogen carrier.
When broken down, it releases hydrogen gas, which may help in future hydrogen-fuel systems.
9. Comparing Esterification and Hydrolysis
| Feature | Esterification | Hydrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Builds an ester | Breaks an ester |
| Needs | Acid catalyst, low water | Acid or base, extra water |
| Main Equation | HCOOH + CH₃OH → HCOOCH₃ + H₂O | HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH |
| Direction | Forward | Reverse |
| Main Product | Ester + Water | Acid + Alcohol |
| Used For | Making esters | Producing acids or alcohols |
This shows how chemists can control the reaction by changing water amount, temperature, or catalyst type.
10. Summary
Here is what we have learned about HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O (Methyl Formate + Water):
Main Points
-
It represents methyl formate reacting with water.
-
The products are formic acid and methanol.
-
The reaction can go both ways — hydrolysis or esterification.
-
Catalysts and temperature control how fast and in which direction it goes.
-
It is widely used in industry, research, and green energy.
Environmental View
-
Low pollution and easy to recycle.
-
Safer than many older solvents.
-
Important example of green, sustainable chemistry.
11. Conclusion
The reaction between methyl formate and water is simple but powerful.
It shows how small organic molecules can change form and be used in many ways — from making formic acid to helping store hydrogen for clean fuel.
This reaction teaches basic ideas like:
-
Chemical equilibrium
-
Catalysis
-
Sustainable production
Even though the keyword HCOOCH CH2 H2O looks complex, it actually represents one of the simplest and most useful reactions in chemistry.
It connects science, industry, and environmental care — showing that chemistry can be both practical and green.