Azelaic Acid for Acne: Benefits and How to Use it for Clear Skin
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide. While there are numerous treatments available, finding the right one for your skin can be a challenge. Among the array of acne-fighting ingredients, azelaic acid has gained increasing attention due to its versatility, efficacy, and relatively mild side effects. Azelaic acid is often seen as a multi-tasking ingredient that can address not only acne but also hyperpigmentation, rosacea, and skin texture issues.
This blog will explore azelaic acid’s benefits for acne, its mechanism of action, and how to use it effectively to achieve clearer skin. Whether you’re new to skincare or looking for alternatives to harsher treatments, azelaic acid might just be the key to unlocking a more even, radiant complexion.
What is Azelaic Acid?
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid that is found in grains like wheat, barley, and rye. While it’s naturally present in small amounts in these foods, the azelaic acid used in skincare products is typically synthesized in labs for higher purity and consistency. In the realm of dermatology, azelaic acid is considered a unique ingredient because of its ability to address multiple skin concerns with fewer risks of irritation compared to other acne treatments.
Azelaic acid is primarily used to treat acne, rosacea, and hyperpigmentation. Available in various concentrations (typically ranging from 10% to 20%), azelaic acid can be found in over-the-counter formulations as well as in prescription-strength products. Its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and exfoliating properties make it a popular choice for those looking to improve overall skin clarity.
How Azelaic Acid Works for Acne
Acne is caused by a combination of factors including excess oil production, clogged pores, the proliferation of bacteria like Cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as Propionibacterium acnes), and inflammation. Azelaic acid tackles several of these contributing factors, making it an effective treatment for mild to moderate acne.
1. Antibacterial Properties
One of the leading causes of acne is the overgrowth of bacteria on the skin, particularly Cutibacterium acnes. This bacteria thrives in the clogged pores and oily environment created by acne, leading to inflammation, pustules, and cysts. Azelaic acid works by inhibiting the growth of these bacteria, reducing the likelihood of breakouts.
Unlike harsher antibacterial treatments like benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid does not cause bacterial resistance, meaning it can be used long-term without diminishing effectiveness.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Action
Inflammation plays a key role in the development of acne, particularly in more severe forms like cystic or nodular acne. Azelaic acid’s anti-inflammatory properties help calm the redness, swelling, and irritation associated with inflamed acne lesions. By reducing inflammation, azelaic acid helps prevent acne from becoming more severe and allows existing acne to heal more quickly.
This makes azelaic acid a great option for those with sensitive or rosacea-prone skin, as it addresses both redness and breakouts without causing further irritation.
3. Exfoliation and Keratolytic Effects
Azelaic acid is also mildly keratolytic, which means it helps to gently exfoliate the skin by encouraging the turnover of dead skin cells. When dead skin cells accumulate, they can clog pores and contribute to acne formation. Azelaic acid works to prevent this by promoting a smoother, clearer skin surface.
Unlike alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), which are often used for exfoliation, azelaic acid is less likely to cause irritation or peeling, making it ideal for those with sensitive or reactive skin.
4. Regulating Melanin Production
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a common aftermath of acne, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones. Azelaic acid helps to lighten these dark spots by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. By controlling melanin overproduction, azelaic acid can help fade the dark marks left behind by acne, giving your skin a more even tone over time.
This dual action of treating acne and hyperpigmentation makes azelaic acid a valuable addition to the skincare routines of those looking to address both concerns simultaneously.
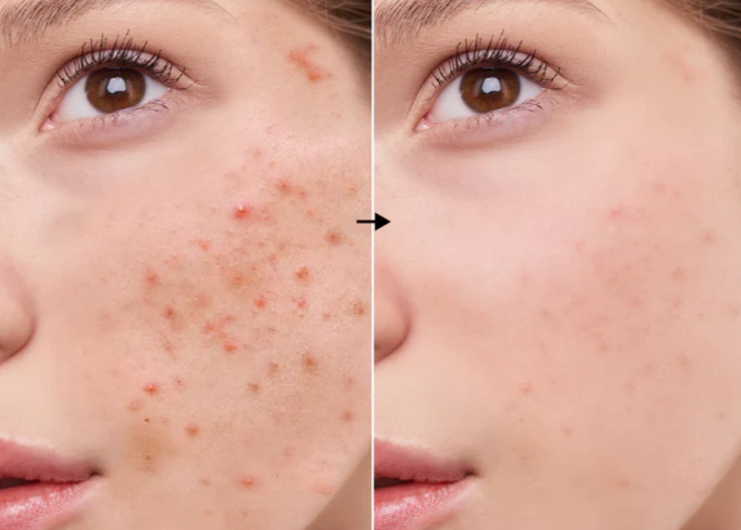

Benefits of Azelaic Acid for Acne-Prone Skin
Azelaic acid offers a host of benefits, not just for managing acne, but also for improving overall skin health. Let’s take a closer look at the key benefits:
1. Gentle Yet Effective
One of the standout benefits of azelaic acid is its gentleness. Many acne treatments, particularly those containing retinoids, salicylic acid, or benzoyl peroxide, can cause significant dryness, redness, or irritation. Azelaic acid, on the other hand, is much less likely to provoke these side effects, making it suitable for sensitive skin types and those prone to redness or rosacea.
2. Reduces Acne Scarring and Hyperpigmentation
As mentioned earlier, azelaic acid is a powerful ingredient for fading post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and acne scars. This makes it a great option for individuals who are not only dealing with active acne but are also trying to address the dark spots and uneven skin tone that often accompany it.
3. Targets Multiple Types of Acne
Azelaic acid is effective against different types of acne, including:
- Comedonal Acne: Whiteheads and blackheads caused by clogged pores.
- Inflammatory Acne: Red, inflamed bumps or pustules.
- Cystic Acne: Deeper, more painful cysts that can lead to scarring.
While azelaic acid may not be strong enough on its own to tackle severe cystic acne, it can still provide relief for milder cases or be used in conjunction with other treatments.
4. Non-Comedogenic
Many acne treatments can sometimes clog pores, exacerbating the issue they are meant to treat. Azelaic acid, however, is non-comedogenic, meaning it won’t block pores. This makes it an excellent choice for individuals who are prone to clogged pores or have oily, acne-prone skin.
5. Safe for Long-Term Use
One of the challenges with some acne treatments is that they can’t be used indefinitely, either because they lose effectiveness or because they pose long-term risks. Azelaic acid is safe for long-term use, making it a viable option for those who need ongoing management of their acne or hyperpigmentation.
How to Use Azelaic Acid for Clear Skin
Now that we’ve covered the benefits, let’s explore how to incorporate azelaic acid into your skincare routine for maximum effectiveness. While azelaic acid is relatively gentle, it’s still important to use it correctly to avoid any potential irritation.
1. Choose the Right Formulation
Azelaic acid is available in various forms, including creams, gels, and serums. You can find it in over-the-counter products with concentrations typically ranging from 10% to 15%, while prescription-strength formulations can go up to 20%. The form you choose will depend on your skin type and the severity of your acne:
- Gels: Best for oily or acne-prone skin as they are lightweight and quickly absorbed.
- Creams: Ideal for normal to dry skin types, as they provide more hydration.
- Serums: Good for layering under moisturizers or other treatments, providing a concentrated dose of active ingredients.
If you’re looking for high-quality azelaic acid products, you can explore Azelaic Acid Cream 10-20% for both over-the-counter and prescription-strength options to suit your skincare needs.
2. Start Slowly
If you’re new to azelaic acid or have sensitive skin, start by applying it once a day, preferably in the evening. Over time, you can increase usage to twice daily (morning and night), as tolerated.
Azelaic acid should be applied after cleansing and toning but before moisturizing. If using in the morning, make sure to follow up with a broad-spectrum sunscreen, as azelaic acid can make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
3. Layering with Other Active Ingredients
Azelaic acid can be combined with other acne treatments, but it’s essential to be mindful of how you layer active ingredients to avoid irritation. Here’s how azelaic acid pairs with other common skincare actives:
- With Retinoids: Retinoids and azelaic acid can be used together, but it’s best to introduce them gradually, alternating between the two at night. If irritation occurs, use one in the evening and the other in the morning.
- With Salicylic Acid or Benzoyl Peroxide: These can be combined with azelaic acid for a more robust acne-fighting routine, but be cautious, as both salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide can be drying. Start slowly and monitor your skin’s response.
- With Niacinamide: This pairing works exceptionally well. Niacinamide helps to soothe and hydrate the skin, which can counterbalance any potential irritation from azelaic acid. It’s a great ingredient to layer alongside azelaic acid in both the morning and evening.
- With Vitamin C: Vitamin C and azelaic acid are both potent brighteners, but they should be used with caution together, especially if you have sensitive skin. If you choose to use both, apply Vitamin C in the morning and azelaic acid at night.
4. Consistency is Key
Azelaic acid is not a quick fix. While you may start to see improvements in your skin’s texture and acne within 4 to 6 weeks, significant changes in hyperpigmentation and overall skin clarity may take longer—sometimes 3 to 6 months. Patience and consistency are crucial when using azelaic acid for acne.
Side Effects and Precautions
Although azelaic acid is considered gentle, especially compared to other acne treatments, some individuals may still experience mild side effects, particularly when first starting the treatment.
Common Side Effects:
- Mild itching or tingling
- Redness or irritation at the application site
- Dryness or flakiness
These side effects are typically temporary and should subside as your skin gets used to the product. To minimize irritation, start by using azelaic acid once daily and gradually increase to twice daily.
When to Avoid Azelaic Acid:
- Hypersensitivity: If you have a known sensitivity to azelaic acid or any of its ingredients, avoid using it.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While azelaic acid is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment during this time.
If you experience severe irritation, persistent redness, or swelling, discontinue use and consult a dermatologist. Ulcuprazol

Who Should Use Azelaic Acid?
Azelaic acid is suitable for a wide range of skin types, but it’s particularly beneficial for:
- People with mild to moderate acne: Whether you struggle with occasional breakouts or more persistent acne, azelaic acid can help reduce both the frequency and severity of pimples.
- Individuals with sensitive skin: If you’ve had negative reactions to harsher acne treatments like retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, or strong acids, azelaic acid offers a gentler alternative that still delivers results.
- Those dealing with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: If dark spots and acne scars are your primary concern, azelaic acid can help lighten them while preventing new breakouts.
- Rosacea sufferers: Because of its anti-inflammatory properties, azelaic acid is also a popular treatment for rosacea, helping to reduce redness, bumps, and skin irritation associated with the condition.
Conclusion
Azelaic acid is a powerhouse ingredient that not only addresses acne but also tackles a variety of skin concerns like hyperpigmentation, redness, and uneven texture. Its gentle yet effective nature makes it suitable for all skin types, particularly those who may have struggled with irritation from other acne treatments.
By consistently incorporating azelaic acid into your skincare routine and combining it with other complementary ingredients like niacinamide or retinoids, you can achieve clearer, more even-toned skin over time. Whether you’re dealing with mild breakouts or more persistent acne issues, azelaic acid offers a well-rounded solution that is safe for long-term use and can help you achieve your skin goals.
As always, if you’re unsure about which products to use or how to incorporate azelaic acid into your regimen, it’s a good idea to consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice.